Your Gastrointestinal perforation pathophysiology images are ready in this website. Gastrointestinal perforation pathophysiology are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Gastrointestinal perforation pathophysiology files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for gastrointestinal perforation pathophysiology pictures information linked to the gastrointestinal perforation pathophysiology keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website frequently gives you suggestions for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
Gastrointestinal Perforation Pathophysiology. Intestinal perforation defined as a loss of continuity of the bowel wall is a potentially devastating complication that may result from a variety of disease processes. Common causes of perforation include trauma instrumentation inflammation infection malignancy ischemia and. Common causes of perforation include trauma instrumentation inflammation infection malignancy ischemia and. This article looks at.
 Evaluation And Mangement Of Intestinal Obstruction American Family Physician From aafp.org
Evaluation And Mangement Of Intestinal Obstruction American Family Physician From aafp.org
Gastrointestinal perforation may occur at any anatomical location from the upper oesophagus to the anorectal junction. Symptoms develop suddenly with severe pain followed shortly by signs of shock. Perforated peptic ulcer pain may track to the right lower quadrant and mimic appendicitis but the onset is more sudden and the child is sicker than. Gastrointestinal perforation is when the gastrointestinal tract loses continuity. Anemia bleeding perforation Cancer development is rare and connected to gastritis. Hematemesis ie vomiting of bright red blood if the source is gastrointestinal is most likely due to a source proximal to the ligament of TreitzMelena ie black tarry stool is most often due to upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
Perforation of an organ can be caused by a variety of factors.
Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Pathophysiology of the digestive system Digestive system overview. Perforated peptic ulcer pain may track to the right lower quadrant and mimic appendicitis but the onset is more sudden and the child is sicker than. Heterogeneity is the most important consideration in the pathophysiology of peptic ulcer disease. Kidney transplant - After a kidney transplant gastrointestinal GI perforations may occur as a complication. The second main symptom of gastrointestinal pathology is bleeding The character of the blood can help identify the source. These contents can range from highly acidic gastric contents in more proximal bowel perforation to fecal material from a more distal area of perforation.
 Source: dovemed.com
Source: dovemed.com
Perforation of the gastrointestinal tract can be due to many causes but main causes are instrumentation during surgery or bowel obstruction. If they heal there is no predictable recurrence. Gastrointestinal perforation GP occurs when a hole forms all the way through the stomach large bowel or small intestine. Gastrointestinal perforation is often the end stage of obstructing inflammatory or ischemic disorders. 2 Most frequent GI disorders.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Delay in resuscitation and definitive surgery will progress rapidly into septic shock multi organ dysfunction and death hence it should be one of the first diagnoses considered in all patients who present with acute abdominal pain. 2 Most frequent GI disorders. This condition can easily develop into serious complications that could result in death. It is a serious condition that often requires emergency surgery. Intestinal perforation defined as a loss of continuity of the bowel wall is a potentially devastating complication that may result from a variety of disease processes.
 Source: calgaryguide.ucalgary.ca
Source: calgaryguide.ucalgary.ca
Hematemesis ie vomiting of bright red blood if the source is gastrointestinal is most likely due to a source proximal to the ligament of TreitzMelena ie black tarry stool is most often due to upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastrointestinal perforation is often the end stage of obstructing inflammatory or ischemic disorders. Symptoms develop suddenly with severe pain followed shortly by signs of shock. Pathophysiology and prevention of diverticulitis and perforation. This condition can easily develop into serious complications that could result in death.
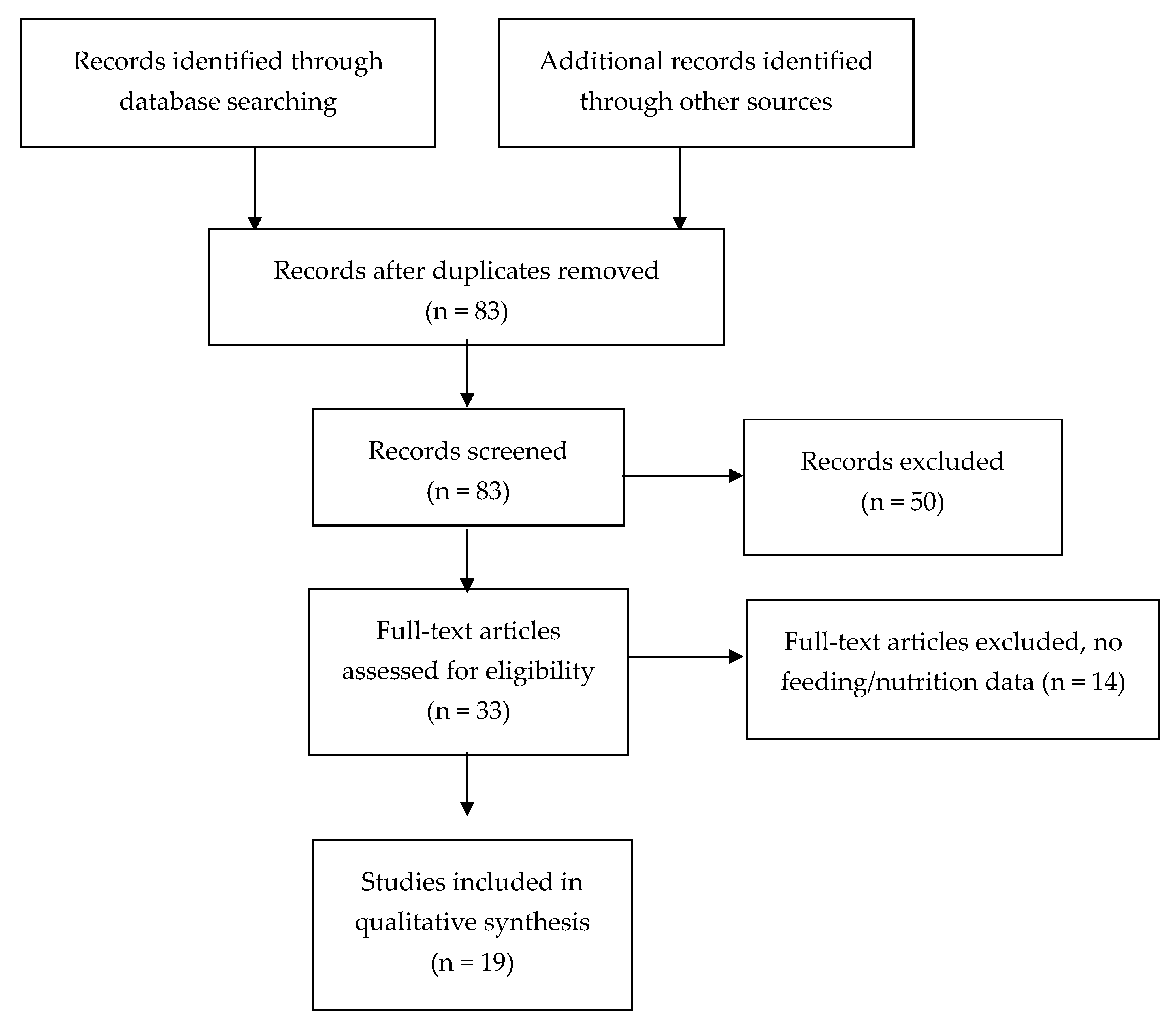 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Gastrointestinal perforation may occur at any anatomical location from the upper oesophagus to the anorectal junction. Pathophysiology Perforation requires full-thickness injury of the bowel wall. Kidney transplant - After a kidney transplant gastrointestinal GI perforations may occur as a complication. It is a serious condition that often requires emergency surgery. Any part of the gastrointestinal tract may become perforated releasing gastric or intestinal contents into the peritoneal space.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Gastrointestinal perforation is a hole in the wall of the stomach small intestine or large bowel. It can be due to a. Symptoms develop suddenly with severe pain followed shortly by signs of shock. Delay in resuscitation and definitive surgery will progress rapidly into septic shock multi organ dysfunction and death hence it should be one of the first diagnoses considered in all patients who present with acute abdominal pain. This condition can easily develop into serious complications that could result in death.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
The second main symptom of gastrointestinal pathology is bleeding The character of the blood can help identify the source. Gastrointestinal perforation is often the end stage of obstructing inflammatory or ischemic disorders. Delay in resuscitation and definitive surgery will progress rapidly into septic shock multi organ dysfunction and death hence it should be one of the first diagnoses considered in all patients who present with acute abdominal pain. This problem may occur in the esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum or gallbladder. Perforation of the gastrointestinal tract can be due to many causes but main causes are instrumentation during surgery or bowel obstruction.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This condition can easily develop into serious complications that could result in death. A penetration B perforation C bleeding D - stenosis Penetrating and perforating ulcers. Hematemesis ie vomiting of bright red blood if the source is gastrointestinal is most likely due to a source proximal to the ligament of TreitzMelena ie black tarry stool is most often due to upper gastrointestinal bleeding. These contents can range from highly acidic gastric contents in more proximal bowel perforation to fecal material from a more distal area of perforation. It can be due to a.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
These contents can range from highly acidic gastric contents in more proximal bowel perforation to fecal material from a more distal area of perforation. Free perforation occurs when bowel contents spill freely into the abdominal cavity causing diffuse peritonitis eg duodenal or gastric perforation. Perforation is heralded by sudden abdominal pain with subsequent signs of peritonitis. Perforated peptic ulcer pain may track to the right lower quadrant and mimic appendicitis but the onset is more sudden and the child is sicker than. Both blunt and penetrating trauma can result in perforation of any part of the gastrointestinal tract see table Some Causes of Gastrointestinal Tract Perforation Some Causes of Gastrointestinal Tract Perforation Any part of the gastrointestinal tract may become perforated releasing gastric or intestinal contents into the peritoneal space.
 Source: dovemed.com
Source: dovemed.com
Perforation is a hole that develops through the wall of a body organ. Gastrointestinal perforation may occur at any anatomical location from the upper oesophagus to the anorectal junction. In these cases the perforation is usually related to the use of high doses of immunosuppressive medications a treatment employed in the early postoperative period and in the management of acute rejection episodes. 2 Most frequent GI disorders. Perforation of an organ can be caused by a variety of factors.
 Source: resources.wfsahq.org
Source: resources.wfsahq.org
Symptoms develop suddenly with severe pain followed shortly by signs of shock. Diagnosis is usually made by the presence of free air in the abdomen on imaging studies. Gastrointestinal perforation is when the gastrointestinal tract loses continuity. Hematemesis ie vomiting of bright red blood if the source is gastrointestinal is most likely due to a source proximal to the ligament of TreitzMelena ie black tarry stool is most often due to upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Bowel perforation results from a violation of the mucosal layers of the intestinal tract resulting in the spilling of air and digestive contents into the peritoneal cavity.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Heterogeneity is the most important consideration in the pathophysiology of peptic ulcer disease. This condition can easily develop into serious complications that could result in death. Acute ulcers and erosions present clinically with gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation. Perforation is a hole that develops through the wall of a body organ. Pathophysiology of gastrointestinal perforation Perforation is full-thickness injury of the bowel wall.
 Source: aafp.org
Source: aafp.org
If they heal there is no predictable recurrence. Free perforation occurs when bowel contents spill freely into the abdominal cavity causing diffuse peritonitis eg duodenal or gastric perforation. 2 Most frequent GI disorders. Bowel perforation results from a violation of the mucosal layers of the intestinal tract resulting in the spilling of air and digestive contents into the peritoneal cavity. Perforation of an organ can be caused by a variety of factors.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The pathophysiology of peptic ulcer disease. It can be due to a. Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Pathophysiology of the digestive system Digestive system overview. Intestinal perforation defined as a loss of continuity of the bowel wall is a potentially devastating complication that may result from a variety of disease processes. It is a serious condition that often requires emergency surgery.

Hematemesis ie vomiting of bright red blood if the source is gastrointestinal is most likely due to a source proximal to the ligament of TreitzMelena ie black tarry stool is most often due to upper gastrointestinal bleeding. This problem may occur in the esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum or gallbladder. Symptoms develop suddenly with severe pain followed shortly by signs of shock. Heterogeneity is the most important consideration in the pathophysiology of peptic ulcer disease. Common causes of perforation include trauma instrumentation inflammation infection malignancy ischemia and.
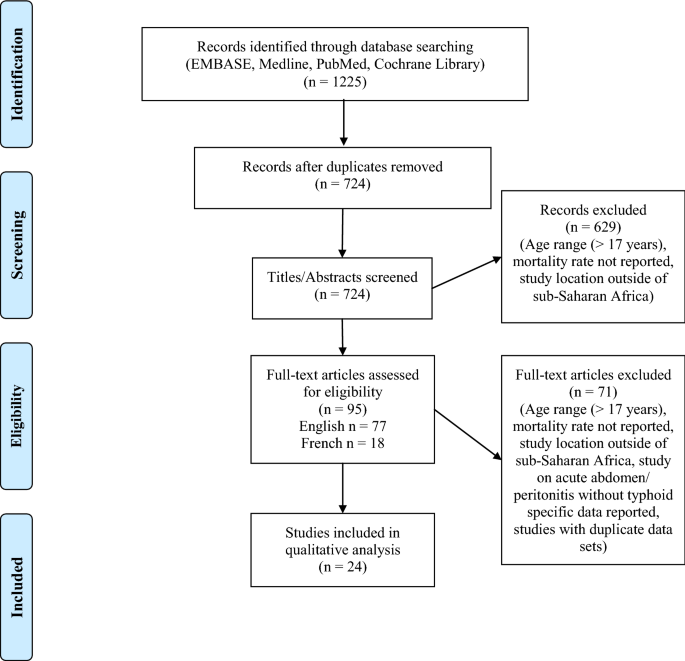 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Any part of the gastrointestinal tract may become perforated releasing gastric or intestinal contents into the peritoneal space. Both blunt and penetrating trauma can result in perforation of any part of the gastrointestinal tract see table Some Causes of Gastrointestinal Tract Perforation Some Causes of Gastrointestinal Tract Perforation Any part of the gastrointestinal tract may become perforated releasing gastric or intestinal contents into the peritoneal space. It is a serious condition that often requires emergency surgery. Symptoms develop suddenly with severe pain followed shortly by signs of shock. Kidney transplant - After a kidney transplant gastrointestinal GI perforations may occur as a complication.
 Source: amhsr.org
Source: amhsr.org
Contained perforation occurs when a full-thickness hole is created by an ulcer but free spillage is prevented because contiguous organs wall off the area as occurs for example when a duodenal ulcer penetrates. Common causes of perforation include trauma instrumentation inflammation infection malignancy ischemia and. Heterogeneity is the most important consideration in the pathophysiology of peptic ulcer disease. Diagnosis is usually made by the presence of free air in the abdomen on imaging studies. Gastrointestinal perforation is a hole in the wall of the stomach small intestine or large bowel.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Pathophysiology of the digestive system Digestive system overview. The pathophysiology of peptic ulcer disease. These contents can range from highly acidic gastric contents in more proximal bowel perforation to fecal material from a more distal area of perforation. Gastrointestinal perforation is often the end stage of obstructing inflammatory or ischemic disorders. Delay in resuscitation and definitive surgery will progress rapidly into septic shock multi organ dysfunction and death hence it should be one of the first diagnoses considered in all patients who present with acute abdominal pain.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Pathophysiology of the digestive system Digestive system overview. Gastrointestinal perforation GP occurs when a hole forms all the way through the stomach large bowel or small intestine. Intestinal perforation defined as a loss of continuity of the bowel wall is a potentially devastating complication that may result from a variety of disease processes. 2 Most frequent GI disorders. This problem may occur in the esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum or gallbladder.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title gastrointestinal perforation pathophysiology by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





